Phosphatidylserine (PS) is one of the prevailing phospholipid components of the biological membranes. It contains two negative and one positive charge resulting in a negative net charge. However, the positive ammonium, with its capacity to form hydrogen bonded attractive electrostatic interactions with the neighboring phosphate residues in the relatively low dielectric domain, bestows on the PS containing bilayers a very rigid structure which determines the spacing between the hydrocarbon chains. Even in the gel phase below the phase transition when the hydrocarbon chains of other phospholipids are in a predominantly trans conforma-tion, the CH2 wagging vibration spectra as measured by FTIR, show a high degree of double gauche conformation. This is compatible only with helical multigauche conformation of the chains as depicted in Fig. 1. The multigauche helices are occasionally interrupted by a single trans conformation which can be detected in the I.R. spectrum as a kink.
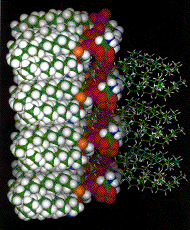
Fig. 1: Interaction between juxtaposed headgroups of two PS bilayers.
These unique interactions between the head groups with their bearing on the conformation of the hydrocarbon chains have also a pronounced effect on the interaction of PS with cholesterol, with ethanol and with different anesthetics investigated by Dr. D. Bach from our department.
If parallelly oriented multibilayers of PS are kept in the presence of water and at the same time their spontaneous vesiculation is prevented by different means, the FTIR spectra of the head groups change with time, indicating a pronounced change in their conformation. Concurrently the rate of exchange of protons by deuterium in the ammonium residues, determined by changes in the vibration spectra of ammonium and of carboxylate, decreases by more than four orders of magnitude and the hydrocarbon helicity monitored by the increase in double gauche conformers is augmented.
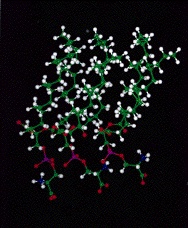
The results are explained by interaction between head groups of juxtaposed polar layers as shown in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2: Schematic representation of a PS monolayer with inter-molecular electrostatic interaction with hydrogen bonding.
Recent Publications:
Brumfeld, V., Bach, D. and Miller, I.R. (1991) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of aqueous dispersions of phosphatidylserine-cholesterol mixtures. Eur. Biophys. J. 19: 287-293.
Miller, I.R. & E. Wachtel (1998) Interbilayer interaction and deuterium- proton exchange in thin films of phosphatidyl serine. Bioelectrochem. & Bioenerg. 45: 203-214.
Bach, D. and I.R. Miller (1998) Hydration of phospholipid bilayers in the presence and absence of cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1368:216-224.
Miller, I.R. and D. Bach (1999) Hydration of phosphatidyl serine multilayers and its modulation by conformational change induced by correlated electrostatic interaction. Bioelectrochem. Bioenrg. 48:361-367.
Miller, I.R. & M. Eisenstein (2000) Structure of phosphatidyl serin (PS) involved in interbilayer salt bridging and hydrogen bonding. Bioelectrochem & Bioenerg. 52: 77-81.
Miller, I.R. D. Bach (2000). Organization of water molecules by adhering to oriented layers of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylserine in the presence of varying concentrations of cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1468, 199-202.
Miller, I.R., Bach, D., Wachtel, E.J., Eisenstein, M. (2001) Competition between hydration and interheadgroup interaction in phospholipid bilayers. Submitted.
Miller, I.R. Effect of Electric Fields on the Structure of Phosphatidyl Choline (PC) in a Multibilayer System. Submitted.
Bach, D. and Miller, I.R. (2001) Attenuated Total Reflection (ATR) FTIR Spectroscopy of Dimyristoyl Phosphatidylserine-Cholesterol Mixtures. Submitted.
Wachtel, E.J., Borochov, N., Bach, D. and Miller, I.R. (2000) The effect of ethanol on the structure of phosphatidylserine bilayers. Submitted.