Table of Contents
Pictures and Concepts
-
The Time Dependent Schrödinger Equation
- Separation of Variables and Reconstitution of the Wavepacket
- Expectation Values
- A Worked Example: Particle in Half a Box
-
The Free Particle Wave Packet
- General Solution
- The Center of the Wavepacket
- The Dispersion of the Wavepacket
The Gaussian Wavepacket
- The Gaussian Free Particle
- General Properties of Gaussian Wavepackets
- Gaussian in a Quadratic Potential
- Reexamination of the Stationary Phase Method
Classical-Quantum Correspondence
- Ehrenfest's Theorem
- Bohmian Mechanics and the Classical Limit
- Fractional Revivals
The Wigner Representation
- The Concept of Phase Space
- The Wigner Representation of Wavepackets
- The Density Operator
- Wigner Representation of the Density Operator
Correlation Functions and Spectra
- Spectra as Fourier Transforms of Wavcpackct Correlation Functions
- General Properties of Fourier Transforms
- Eigenfunctions as Fourier Transforms of Wavepackets
One Dimensional Barrier Scattering
- Wavepacket Formulation of Reflection and Transmission Coefficients
- Cross-Correlation Function Formulation
- Scattering Eigenstates
- Reconstituting the Wavepacket from the Scattering Eigenstates
- Resonances and Time Delay
Formal Theory and Methods of Approximation
Linear Algebra and Quantum Mechanics
- Linear Vector Spaces
- Operators: Mapping a Wavefunction to Another Wavefunction
- Discrete Basis Sets
- Continuous Basis Sets
Approximate Solutions
- The Schrödingcr, Heisenberg and Interaction Pictures
- Time Dependent Perturbation Theory
- The Magnus Expansion
- Adiabatic Dynamics and the Geometrical Phase
- Periodic Hamiltonians and Floquet Theory
- Variational Principles and the Time-Dependent Hartree Approximation
Semiclassical Mechanics
- The Classical Action
- Path Integration
- The van Vleck Propagator
- The Propagator as a Unitary Transformation
- Gaussian Wavepackcts and the van Vleck Propagator
Numerical Methods
- Spectral and Pseudospectral Representation
- Pscudospectral Calculation of Matrix Elements
- Discrete Variable Represenation
- The Fourier Method
- Time Propagation
Applications
Introduction to Molecular Dynamics
- The Born-Oppenheimer Approximation
- Adiabatic vs. Diabatic Representations
- Potential Energy Surfaces
- Normal Modes of Vibration
- Chemical Reactions and Transition State Theory
- Symmetry and Permutations
- Hyperspherical Coordinates
Femtosecond Pulse Pair Excitation
- First Order Processes: Wavepacket Interferometry
- Second Order Processes: Clocking Chemical Reactions
- Coherent Nonlinear Spectroscopy
- Density Operator Formulation of Optical Perturbations
One- and Two-Photon Electronic Spectroscopy
- Electronic Absorption and Emission Spectroscopy
- Transition State Spectroscopy
- Resonance Raman Spectroscopy
- Dispersed Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Strong Field Excitation
- Two-level system
- The Feynman-Vernon-Hellwarth (FVH) Representation
- Adiabatic Excitation: Population transfer in a 3-Level System
- Impulsive Excitation
- Heating and Cooling of Molecular Internal Degrees of Freedom
Design of Femtosecond Poise Sequences to Control Reactions
- Pump-Dump Scheme
- Variational Formulation of Control of Product Formation
- Applications of the Variational Formulation
- Multiple Pathway Interference
- Chirped Pulse Excitation
- Learning Algorithms
Wavepacket Approach to Photodissociation
- Introduction
- The Eigenstates of an Asymptotic Hamiltonian
- The Eigenstates of a Scattering Hamiltonian
- Møller Operators
- Wavcpackct Formulation of Photodissociation
- Applications
Wavepacket Approach to Reactive Scattering
- The Concept of an Arrangement Channel
- Scattering Eigenstates for Multiple Arrangements
- Wavcpackct Cross-Correlation Function Formulation of
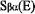
- Application to Collinear
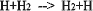
- Cumulative Reaction Probability