Publications
2015
-
(2015) Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 112, 44, p. E6028-E6037 Abstract
Predators feed on prey to acquire the nutrients necessary to sustain their survival, growth, and replication. In Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus, an obligate predator of Gram-negative bacteria, cell growth and replication are tied to a shift from a motile, free-living phase of search and attack to a sessile, intracellular phase of growth and replication during which a single prey cell is consumed. Engagement and sustenance of growth are achieved through the sensing of two unidentified prey-derived cues. We developed a novel ex vivo cultivation system for B. bacteriovorus composed of prey ghost cells that are recognized and invaded by the predator. By manipulating their content, we demonstrated that an early cue is located in the prey envelope and a late cue is found within the prey soluble fraction. These spatially and temporally separated cues elicit discrete and combinatory regulatory effects on gene transcription. Together, they delimit a poorly characterized transitory phase between the attack phase and the growth phase, during which the bdelloplast (the invaded prey cell) is constructed. This transitory phase constitutes a checkpoint in which the late cue presumably acts as a determinant of the prey's nutritional value before the predator commits. These regulatory adaptations to a unique bacterial lifestyle have not been reported previously.
-
(2015) The Journal of Cell Biology. 211, 1, p. 191-203 Abstract
Fusion of individual myoblasts to form multinucleated myofibers constitutes a widely conserved program for growth of the somatic musculature. We have used electron microscopy methods to study this key form of cell-cell fusion during development of the indirect flight muscles (IFMs) of Drosophila melanogaster. We find that IFM myoblast-myotube fusion proceeds in a stepwise fashion and is governed by apparent cross talk between transmembrane and cytoskeletal elements. Our analysis suggests that cell adhesion is necessary for bringing myoblasts to within a minimal distance from the myotubes. The branched actin polymerization machinery acts subsequently to promote tight apposition between the surfaces of the two cell types and formation of multiple sites of cell-cell contact, giving rise to nascent fusion pores whose expansion establishes full cytoplasmic continuity. Given the conserved features of IFM myogenesis, this sequence of cell interactions and membrane events and the mechanistic significance of cell adhesion elements and the actin-based cytoskeleton are likely to represent general principles of the myoblast fusion process.
-
(2015) Cell Reports. 12, 1, p. 7-14 Abstract
Communication between organelles is crucial for eukaryotic cells to function as one coherent unit. Animportant means of communication is through membrane contact sites, where two organelles come into close proximity allowing the transport of lipids and small solutes between them. Contact sites are dynamic in size and can change in response to environmental or cellular stimuli; however, how this is regulated has been unclear. Here, we show that Saccharomyces cerevisiae Lam6 resides in several central contact sites: ERMES (ER/mitochondria encounter structure), vCLAMP (vacuole and mitochondria patch), and NVJ (nuclear vacuolar junction). Weshow that Lam6 is sufficient for expansion of contact sites under physiological conditions and necessary for coordination of contact site size. Given that Lam6 is part of a large protein family and is conserved in vertebrates, our work opens avenues for investigating the underlying principles of organelle communication.
-
(2015) Journal of the American Chemical Society. 137, 23, p. 7429-7440 Abstract
The unique properties of carbon nanotubes (CNT) are advantageous for emerging applications. Yet, the CNT insolubility hampers their potential. Approaches based on covalent and noncovalent methodologies have been tested to realize stable dispersions of CNTs. Noncovalent approaches are of particular interest as they preserve the CNTs structures and properties. We report on hybrids, in which perylene diimide (PDI) amphiphiles are noncovalently immobilized onto single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNT). The resulting hybrids were dispersed and exfoliated both in water and organic solvents in the presence of two different PDI derivatives, PP2b and PP3a. The dispersions were investigated using cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM), providing unique structural insights into the exfoliation. A helical arrangement of PP2b assemblies on SWCNTs dominates in aqueous dispersions, while a single layer of PP2b and PP3a was found on SWCNTs in organic dispersions. The dispersions were probed by steady-state and time-resolved spectroscopies, revealing appreciable charge redistribution in the ground state, and an efficient electron transfer from SWCNTs to PDIs in the excited state. We also fabricated hybrid materials from the PP2b/SWCNT dispersions. A supramolecular membrane was prepared from aqueous dispersions and used for size-selective separation of gold nanoparticles. Hybrid buckypaper films were prepared from the organic dispersions. In the latter, high conductivity results from enhanced electronic communication and favorable morphology within the hybrid material. Our findings shed light onto SWCNT/dispersant molecular interactions, and introduce a versatile approach toward universal solution processing of SWCNT-based materials.
-
(2015) Nature Communications. 6, 7193. Abstract
Cell-wall peptidoglycan (PG) of Gram-positive bacteria is a strong and elastic multi-layer designed to resist turgor pressure and determine the cell shape and growth. Despite its crucial role, its architecture remains largely unknown. Here using high-resolution multiparametric atomic force microscopy (AFM), we studied how the structure and elasticity of PG change when subjected to increasing turgor pressure in live Group B Streptococcus. We show a new net-like arrangement of PG, which stretches and stiffens following osmotic challenge. The same structure also exists in isogenic mutants lacking surface appendages. Cell aging does not alter the elasticity of the cell wall, yet destroys the net architecture and exposes single segmented strands with the same circumferential orientation as predicted for intact glycans. Together, we show a new functional PG architecture in live Gram-positive bacteria.
-
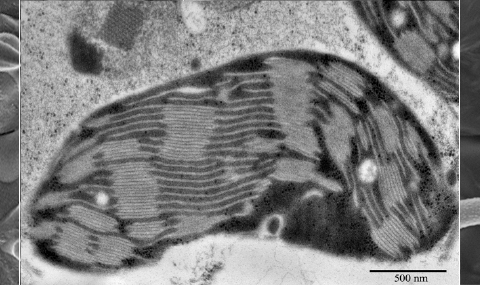
(2015) Plant Physiology. 167, 4, p. 1554-1565 Abstract
During desiccation, homoiochlorophyllous resurrection plants retain most of their photosynthetic apparatus, allowing them to resume photosynthetic activity quickly upon water availability. These plants rely on various mechanisms to prevent the formation of reactive oxygen species and/or protect their tissues from the damage they inflict. In this work, we addressed the issue of how homoiochlorophyllous resurrection plants deal with the problem of excessive excitation/electron pressures during dehydration using Craterostigma pumilum as a model plant. To investigate the alterations in the supramolecular organization of photosynthetic protein complexes, we examined cryoimmobilized, freeze-fractured leaf tissues using (cryo)scanning electron microscopy. These examinations revealed rearrangements of photosystem II (PSII) complexes, including a lowered density during moderate dehydration, consistent with a lower level of PSII proteins, as shown by biochemical analyses. The latter also showed a considerable decrease in the level of cytochrome f early during dehydration, suggesting that initial regulation of the inhibition of electron transport is achieved via the cytochrome b6f complex. Upon further dehydration, PSII complexes are observed to arrange into rows and semicrystalline arrays, which correlates with the significant accumulation of sucrose and the appearance of inverted hexagonal lipid phases within the membranes. As opposed to PSII and cytochrome f, the light-harvesting antenna complexes of PSII remain stable throughout the course of dehydration. Altogether, these results, along with photosynthetic activity measurements, suggest that the protection of retained photosynthetic components is achieved, at least in part, via the structural rearrangements of PSII and (likely) light-harvesting antenna complexes into a photochemically quenched state.