Publications
2022
-
(2022) Cell Systems. 13, 5, p. 408-425.e12 Abstract
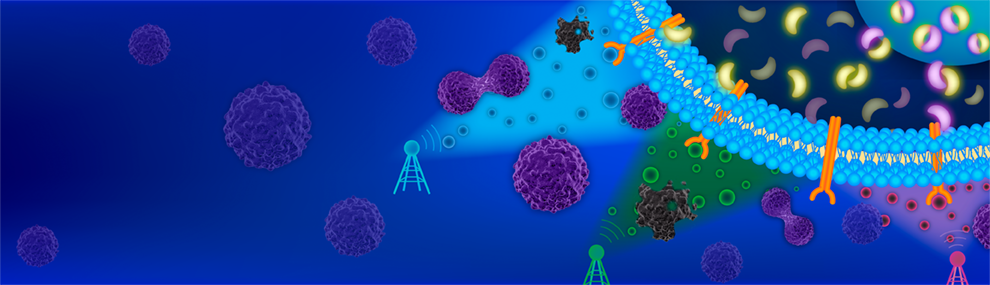
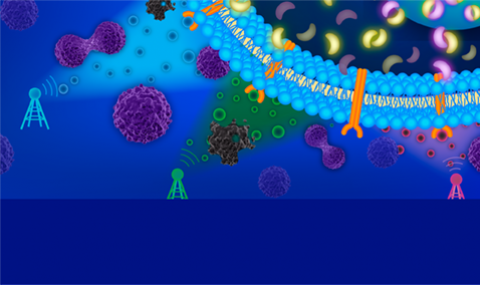
In multicellular organisms, secreted ligands selectively activate, or \u201caddress,\u201d specific target cell populations to control cell fate decision-making and other processes. Key cell-cell communication pathways use multiple promiscuously interacting ligands and receptors, provoking the question of how addressing specificity can emerge from molecular promiscuity. To investigate this issue, we developed a general mathematical modeling framework based on the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathway architecture. We find that promiscuously interacting ligand-receptor systems allow a small number of ligands, acting in combinations, to address a larger number of individual cell types, defined by their receptor expression profiles. Promiscuous systems outperform seemingly more specific one-to-one signaling architectures in addressing capability. Combinatorial addressing extends to groups of cell types, is robust to receptor expression noise, grows more powerful with increases in the number of receptor variants, and is maximized by specific biochemical parameter relationships. Together, these results identify design principles governing cellular addressing by ligand combinations.
-
(2022) Cell Systems. 13, 5, p. 388-407.e10 Abstract
Cell-cell communication systems typically comprise families of ligand and receptor variants that function together in combinations. Pathway activation depends on the complex way in which ligands are presented extracellularly and receptors are expressed by the signal-receiving cell. To understand the combinatorial logic of such a system, we systematically measured pairwise bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) ligand interactions in cells with varying receptor expression. Ligands could be classified into equivalence groups based on their profile of positive and negative synergies with other ligands. These groups varied with receptor expression, explaining how ligands can functionally replace each other in one context but not another. Context-dependent combinatorial interactions could be explained by a biochemical model based on the competitive formation of alternative signaling complexes with distinct activities. Together, these results provide insights into the roles of BMP combinations in developmental and therapeutic contexts and establish a framework for analyzing other combinatorial, context-dependent signaling systems.