Unlocking the mysteries and potential of RNA
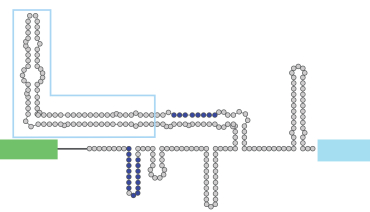
Only 1% of the human genome encodes protein sequences, yet a significant fraction of genetic variants associated with human disease are found in the other 99%. Many of these "noncoding" regions are transcribed into long RNA molecules that remain poorly understood. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) contain at least 200 bases, and are molecularly identical to mRNAs. The human genome contains >20,000 lncRNAs genes, and an increasing portion of them has been implicated as important in a myriad of biological processes, including dosage compensation, transcriptional regulation, and establishment of cell identity. Many of these are dysregulated in human disease, including cancer and neurological disorders. lncRNAs act via diverse and mostly uncharted mechanisms, which are the main current focus of our lab. Our goal is to understand the functionality of lncRNAs and how it manifests itself in their sequences and structures. We are also studying other noncoding RNA fragments such as UTRs, and are generally interested in both the process of transcription and in the post-transcriptional fate of RNA molecules. We study these questions using various systems, including human cell lines and primary cells, mouse embryonic stem cells, and mouse models, and by combining experimental and computational biology.