Artificial Intelligence for Medicine
Super Resolution in Ultrasound and Microscopy
The attainable resolution of ultrasonography and optical imaging is fundamentally limited by diffraction, where the smallest resolvable feature is roughly half the wavelength. Improving resolution can greatly benefit applications such as imaging blood vessels (<100 μm) or cellular organelles (<100 nm).
In our lab, we use sparse frame sequences and model-based learning to surpass this limit. Inspired by a Nobel Prize-winning concept, we localize emitters at sub-diffraction precision and recover the underlying structure across frames. Unlike classical approaches that rely on frame-level separability, our learning-based methods can resolve dense, overlapping structures using fewer frames and in real time.
Our deep-unfolded networks integrate physical models and optimization principles for efficient recovery. These systems support single-frame learning, operate under challenging conditions, and generalize to diverse modalities—from live-cell microscopy to in-vivo ultrasound imaging. As a result, we enable practical super-resolution tools for both biological and clinical applications.
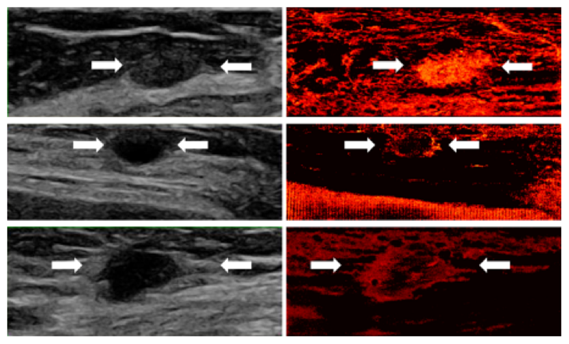
Super-resolution demonstrations in human ultrasound scans show the vascular characteristics of three types of breast lesions:
Top (Fibroadenoma - benign): The super-resolved image reveals an oval, well-circumscribed mass with uniform, dense vascularization.
Middle (Cyst - benign): The recovery highlights peripheral vascular concentration surrounding a round, avascular core.
Bottom (Invasive Ductal Carcinoma - malignant): An irregular, ill-defined mass with sparse central and dense peripheral vasculature.
Super-resolution vascular imaging of three breast lesions: fibroadenoma (top), cyst (middle), and invasive ductal carcinoma (bottom).
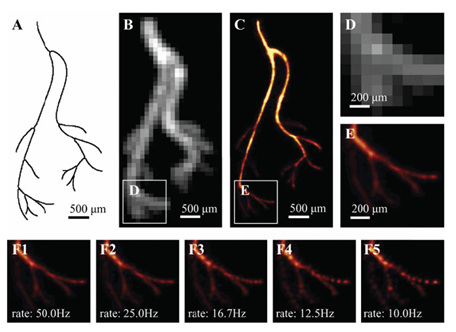
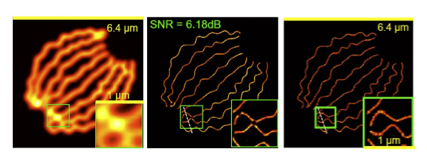
Super-resolution microscopy of biological tubulins: Reconstruction of microtubule structures using 361 high-density frames. The left panel shows a diffraction-limited image; the middle panel presents our learning-based reconstruction, closely matching the right panel ground truth, demonstrating enhanced contrast and sub-diffraction detail recovery.
Tubulin structure recovered from high-density frames. Left: diffraction-limited image. Middle: our reconstruction. Right: ground truth.
References:
- O. Bar-Shira, A. Grubstein, Y. Rapson, D. Suhami, E. Atar, K. Peri-Hanania, R. Rosen, Y. C. Eldar, "Learned Super Resolution Ultrasound for Improved Breast Lesion Characterization", 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2021), October 2021.
- G. Dardikman-Yoffe and Y. C. Eldar, "Learned SPARCOM: Unfolded Deep Super-Resolution Microscopy", Optics Express, vol. 28, issue 19, pp. 27736-27763, September 2020.
- A. Bar-Zion, O. Solomon, C. Tremblay-Darveau, D. Adam and Y. C. Eldar, "SUSHI: Sparsity-Based Ultrasound Super-Resolution Hemodynamic Imaging", IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics and Frequency Control, vol. 65, issue 12, pp. 2365-2380, December 2018.
- O. Solomon, R. J. G. van Sloun, H. Wijkstra, M. Mischi and Y. C. Eldar, "Exploiting Flow Dynamics for Super-Resolution in Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound", IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, vol. 66, issue 10, pp. 1573-1586, October 2019.
- R. J. G. van Sloun, O. Solomon, M. Bruce, Z. Z. Khaing, H. Wijkstra, Y. C. Eldar and M. Mischi, "Super-Resolution Ultrasound Localization Microscopy through Deep Learning", IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 40, issue 3, pp. 829-839, March 2021.
Artificial Intelligence for Medicine
One of our primary areas of interest is to harness model-based AI methods, coupled with signal processing methods and devices, to tackle real-world health challenges. Through strong collaborations with radiologists and clinicians both in Israel and abroad, we identify unmet clinical needs and engage in clinical projects aimed at enhancing early disease detection, develop diagnostic methods that rely on low-cost testing, making them immediately accessible, minimizing diagnostic errors, assisting physicians in their decision-making processes, and developing improved imaging and diagnostic devices with enhanced quality in challenging settings. To this end, we develop methods that integrate the physics and the understanding of the clinical data into our AI and devices. Our focus lies in developing model-based AI techniques that can effectively operate on limited training datasets while producing results that are interpretable and comprehensible. By incorporating domain expertise and understanding into our AI methods, we aim to achieve more reliable and meaningful outcomes in healthcare applications.
Our research topics include
- Multimodal deep learning: combining the information obtained from different imaging modalities in the interest of improved diagnosis. For example, physicians use various imaging modalities for the diagnosis of breast cancer (mammography, ultrasound, MRI), Cardiac diseases (ECG and Xray), diagnosis of Crohn’s disease relapse (Capsule endoscopy, MRI), or Gaucher spline volume estimation (Ultrasound, MRI). In our research, we aim at integrating the information obtained from these different modalities in order to enhance the accuracy of diagnosis.
- Use of AI methods for the analysis of ultrasound “channel data” (the pre-beamformed RF data received at the ultrasound machine): our objective is to extract important tissue properties that can aid in disease diagnosis and assessment, e.g., help determine whether lesions are benign or malignant or help quantify liver fat. By leveraging model-based AI techniques, we strive to uncover meaningful patterns and features within the ultrasound channel data, enabling more accurate and informative diagnostic capabilities.
- Use of AI for conversion between imaging modalities: e.g., using deep learning techniques to synthetically convert ultrasound images into semi-CT images. This synthetic conversion has the potential to provide additional insights and expand the diagnostic capabilities in situations where obtaining CT scans may not be feasible or desirable.
- AI-guided ultrasound image acquisition: We are actively exploring AI-guided image acquisition techniques with the aim of addressing the operator-dependency of ultrasound imaging. By leveraging AI guidance, we aim to enhance the consistency and accuracy of ultrasound imaging, ultimately making it more accessible and enabling non-expert sonographers to produce high-quality scans.
- Deep learning for super-resolution vascular ultrasound imaging: applying model-based deep learning methods for the processing of data received from contrast-enhanced ultrasound, in order to create vascular reconstructions with high resolution with applications in cancer diagnosis or inflammatory diseases.
- Innovative AI diagnostic techniques based on low-cost, accessible testing: enabling rapid detection and broad availability during the COVID-19 pandemic. This approach not only facilitates timely public health responses but also offers significant cost savings at scale, making it a powerful solution for global health challenges.
- AI methods for the use of radar for vital sign monitoring: smart use of the power of AI to refine non-contact vital signs monitoring capabilities.
References:
- A. Amar, A. Grubstein, E. Atar, K. Peri Hanania, N. Glazer, R. Rosen, S. Savariego and Y. C. Eldar, "Deep Task-Based Beamforming and Channel Data Augmentations for Enhanced Ultrasound Imaging", Submitted to IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, February 2025.
- D. Keidar et. al, “COVID-19 Classification of X-ray Images Using Deep Neural Networks”, European Radiology, pp. 1-10, May 2021.
- O. Frank et. al, "Integrating Domain Knowledge into Deep Networks for Lung Ultrasound with Applications to COVID-19", IEEE Transaction on Medical Imaging, vol. 41, issue 3, pp. 571-581, March 2022.
- O. Bar-Shira, A. Grubstein, Y. Rapson, D. Suhami, E. Atar , K. Peri-Hanania, R. Rosen, Y. C. Eldar, "Learned Super Resolution Ultrasound for Improved Breast Lesion Characterization", MICCAI 2021.
- B. Luijten, R. Cohen, F. J. de Bruijn, H. A. W. Schmeitz, M. Mischi, Y. C. Eldar, and R. J. G. Van Sloun, "Adaptive Ultrasound Beamforming Using Deep Learning", IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol. 39, issue 12, pp. 3967-3978, December 2020.
- R. J. G. van Sloun, R. Cohen, Y. C. Eldar, "Deep Learning in Ultrasound Imaging", Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 108, issue 1, pp. 11-29, January 2020.
- T. Sharon and Y. C. Eldar, "Real-Time Model-Based Quantitative Ultrasound and Radar", IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, vol. 10, pp. 1175-1190, August 2024.