MRI Safety and Safety Procedures
The purpose of this document is to provide an easy reference for MRI safety issues, included in the safety course. For more details please also refer to Siemens Safety manual that is available on site and as a pdf, to ACR White Paper on MR Safety, AJR:178, 1335-1352, 2002, and ACR Guidance document on MR Safe Practices:2013 (JMRI 37:501-530,2013) and to http://www.mrisafety.com a site maintained by Frank Shellock.
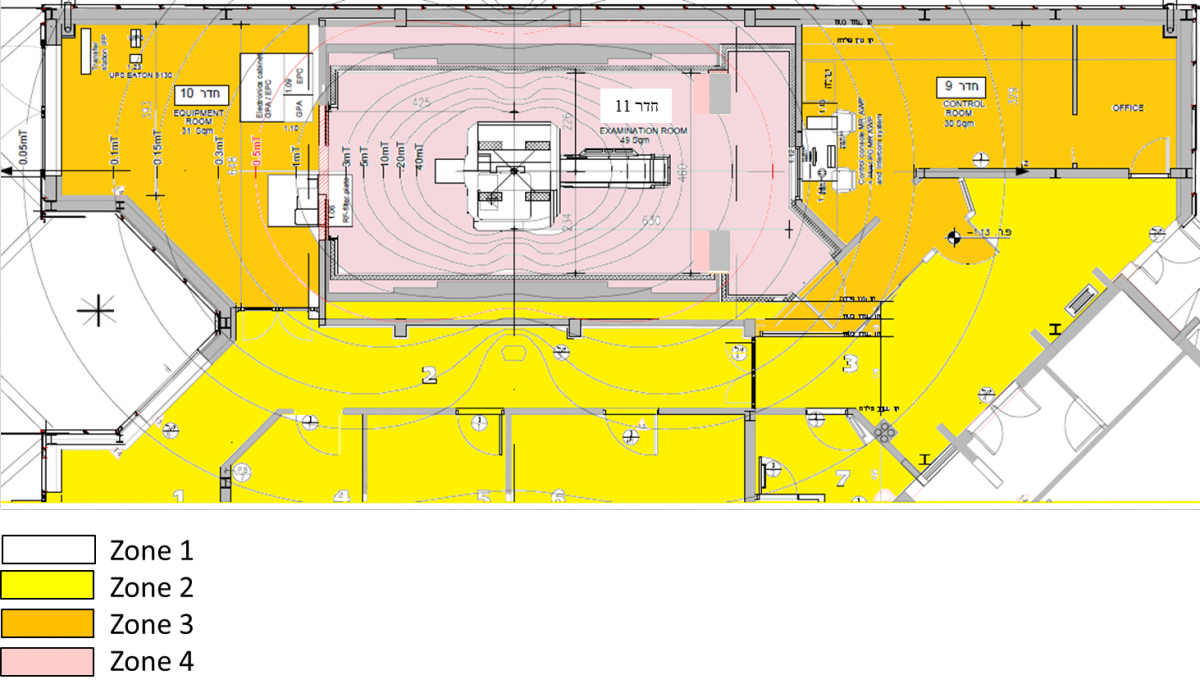
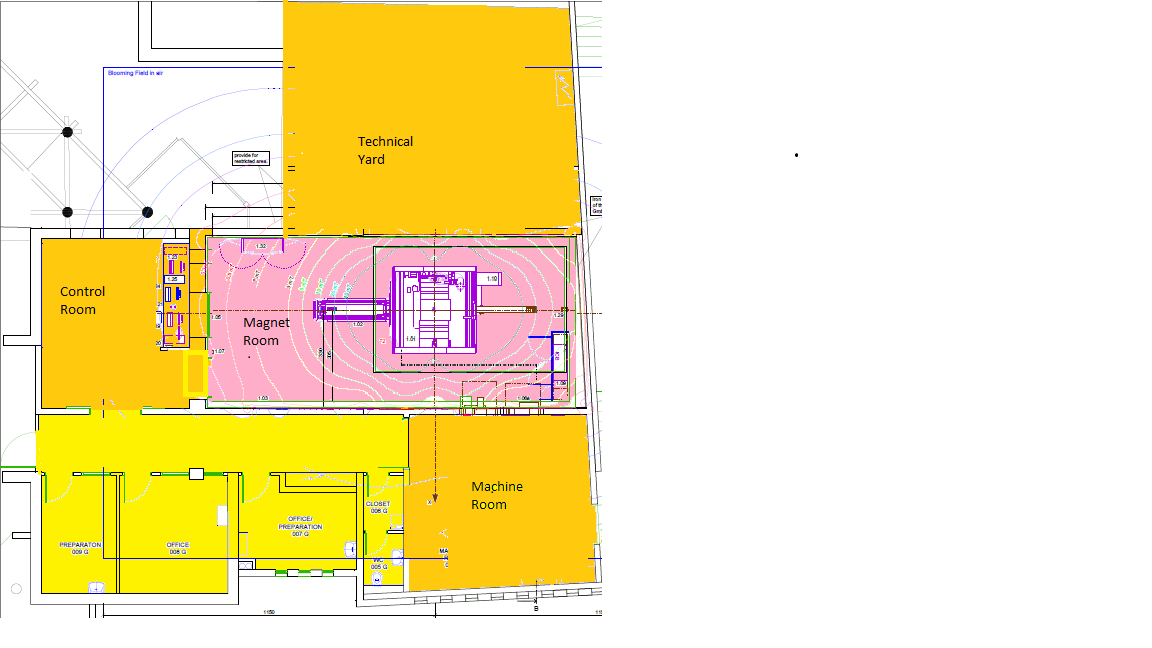
No one may enter the Arison 3 Tesla MRI facility and the Azrieli National institute 7 Tesla MRI facility without authorization from the Weizmann Imaging Center (WIC). The center and surrounding areas are divided into four safety zones as follows:
The Arison 3 Tesla MRI facility:
The Azrieli National institute 7 Tesla MRI facility:
Where :
Zone 1 Includes all areas that are freely accessible to the public, without supervision.
Zone 2 Still a public area, but the interface between unregulated zone 1 and the strictly controlled zones 3 and 4. MR safety screening should occur here under the technologist/certified user supervision.
Zone 3 Contains the control as well as the machine room at the 3T facility and the technical yard at the 7T facility. In the machine room and technical yard fringe fields are sufficiently strong to present a physical hazard to unscreened subjects and personnel. The control rooms are essentially free of risk, however have free, physically unrestricted access to Zone 4 that poses risk.
Zone 4 The MR magnet rooms. Has the highest field and greatest risk and from which ferromagnetic objects must be excluded. In this area fringe, gradient, or RF magnetic fields present a physical hazard to unscreened participants and personnel.
Although not detectable by the human senses, a magnetic field can be dangerous to equipment and to people. Since THE MAGNET IS ALWAYS ON, always “at field” , 24 hrs/day, 365 days /year safety procedures must be followed to prevent accidents.
Due to the high magnetic field, ferromagnetic materials or tools introduced into the proximity of the scanner become projectiles which may present a lethal risk to personnel working in the vicinity of the magnet and to subjects participating in the experiments.
Warning signs are posted on all entrances to the facility and on the door of the scanner, stating that a strong magnetic field is in use. Additional warning signs in the entrance to the magnetic security zones (zones 3 and 4) state that the entrance is restricted to authorized personnel only.
- No one may enter the MRI scan rooms without authorization from the CRP.
The 0.5 mT zone is labeled with a red line on the floor at the entrance to the scanner room
- Never leave the door of the scan room open.
When entering the room, entrance to the room should be restricted by the plastic chain that is attached to the two entrance poles.
- Do not carry or move ferromagnetic objects into the examination room. Objects such as buckets, oxygen tanks, toolboxes, fire extinguishers, chairs, cameras, etc.
- Do not move objects in the scanner room, while a subject is in the scanner.
- Small metal objects (such as: pens, pins, hair clips, scissors, flashlight, phones) are prohibited in the scan room. Do not wear or carry any magnetizable object
The high magnetic field in and around the magnet may disturb the function magnetic implants such as cardiac pacemakers and other implanted electronic devices. Persons with pacemakers or other implanted electronic devices must remain outside the 0.5 mT zone namely, they can not enter the magnet room and the machine room.
Due to risk of injury for personal with metallic implants in their bodies, persons with metallic parts or mechanical implants in their bodies (such as clips, screws, and plates) are prohibited from entering the marked zone – the scanner room as well as the machine room.
Make sure that your subjects are escorted, while attending the facility.
Screening Procedures
The researcher screens the prospective MRI subjects for contraindications at the time an appointment is made (screening form in Hebrew and in English). Absolute contraindications for scanning include: cardiac pacemakers, cochlear (inner ear) implants, previous surgery, ferromagnetic or unidentifiable aneurysm clips, implanted stimulators, metal or unidentifiable foreign bodies in the eyes, IUD (only some are safe), occupational exposure to metal lathe or welding. Additionally, participants are asked during the screening process if there is any chance they may be pregnant. If there is such a chance, they are excluded from the study.
If there is any question regarding a possible risk to the subject, due to his medical history, the WIC staff are to be consulted.
Before entering the scan room, the CRP reviews the subject screening form with the participant, item by item, to ensure that there is no contraindication for scanning. The CRP then witness the subject signing the MRI screening form. Screening will be conducted each time a participant is scanned, regardless of being a repeated participant.
The CRP will then assure that the participant does not have anything in his/her pockets, does not wear a metal jewelry and that any body piercing or medical/nicotine stach was removed.
In any experiment that involves a human subject who is currently a patient, defined as a member of a non-healthy subject population in the Helsinki-approved research, the physician from the medical center that is a partner to the Helsinki must review the subjects screening form and satisfy himself/herself that there is no contraindication for scanning, the physician will also witness the subject signing the MRI screening form.
It is the WIC policy to defer scanning if there is any possibility of causing injury to a subject or staff.
Noise Protection
The MR scanner produces very high acoustic noise levels. The acoustic noise is caused by operating the gradients in conjugation with the static magnetic field.
Prior to scanning, provide ear protection to the subject to reduce the noise level. Researchers that stay in the scan room while the gradient system is on, must also wear hearing protection.
Participant Safety during scanning
- Keep your eyes and ears on the participant at all times. Stay in communication with your participant to identify warming.
Participants should be monitored continuously through the radio frequency-shielded window between the MR scanning room and the control room or by using the IR camera that is located in the scanner room and projects the scanner to the screen above the console. The participant can hear the MRI operator through use of the intercom and can communicate with the operator. Throughout every scanning, an emergency buzzer is placed in the subject's hand, to be present if he/she experiences any pain, discomfort, claustrophobia, or has any other concern. In the event that the buzzer is pressed, scanning is aborted immediately and the subject is removed from the scanner upon his/her request or if needed.
Before running an experiment:
- Check if pressing the squeeze bulb triggers the patient alert.
- Check the Table Stop buttons at the intercom and at the patient table. Ensure that these buttons function properly.
- Check if communication with the subject in the examination room works properly
To date, there is no scientific proof that MR examination are harmless for pregnant women or that RF exposure are harmless for pregnant operating personnel. Therefore, pregnant researchers and staff should not enter the scanning room, while scanning.
Participant Emergencies
Should a condition exist where the patient is having a medical emergency, all efforts must be made to quickly and safely remove the patient from the scan room.
Once the patient is removed from the MR scan room, close the door to prevent re-entry.
Under no circumstances entrance to the scan room without proper screening can be allowed!
Emergency numbers are:
- Weizmann's emergency call 2999
- Shahal – Medical Emergency Service *6767, customer code: 9921002842
If needed, there is an oxygen supply in the magnet room (on it’s walls).
In Zone 2 there is also a first aid kit that is MR unsafe and includes magnetic items so therefore it can be used only outside of the magnet room!! Before working with the system, familiarize yourself with the location of these items.
Do not operate the oxygen bottle, the defibrillator, or other tools for resuscitation in the magnet room !!
Physiologic Effects
During an MR examination, the subject is exposed to three different types of electromagnetic fields: static main magnetic field, gradient fields and radio frequency fields. The effects of these fields vary including the immediate vicinity of the MR system. In addition to the subject, accompanying personnel or operating personnel are subject to these fields in the scanner room.
Static magnetic field effects
A known physical effect of static magnetic field is that they exert forces on moving particles that are electrically charged (e.g. ions). This results in induced electrical currents and directional changes in the way these particles move, which may cause noticeable physiological effects.
If the head is moved rapidly in the proximity of the magnet bore, forces are exerted on the ions in the fluid, causing nerve stimulations, which may result in feeling of dizziness, vertigo, drowsiness, or metallic taste. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid sudden movements when exposed to the strong magnetic field.
Prior to moving into the magnetic field, inform the participant about the possible occurrence of these symptoms.
Time varying magnetic field effects
The low-frequency change of the magnetic flux (switching on and off gradients) induces an electrical field in the tissue of the subject that shifts the charge in the nerve fibers of the tissue. This shift in charge may lead to peripheral nerve stimulation and to muscle stimulation, depending on the strength, frequency, and duration of the shift in charge.
Large current loops caused by skin-to-skin contact for example by crossed hands, knee-knee contact, or ankle-to-ankle contact, may occur if the subject is not positioned correctly. These may enhance the nerve and muscle stimulation.
Therefore, Ensure that the subjects is positioned correctly and is not closing loops.
- Position the participants to avoid skin-to-skin contact (e.g. no hands on hips, no crossed arms, no crossed legs, etc.).
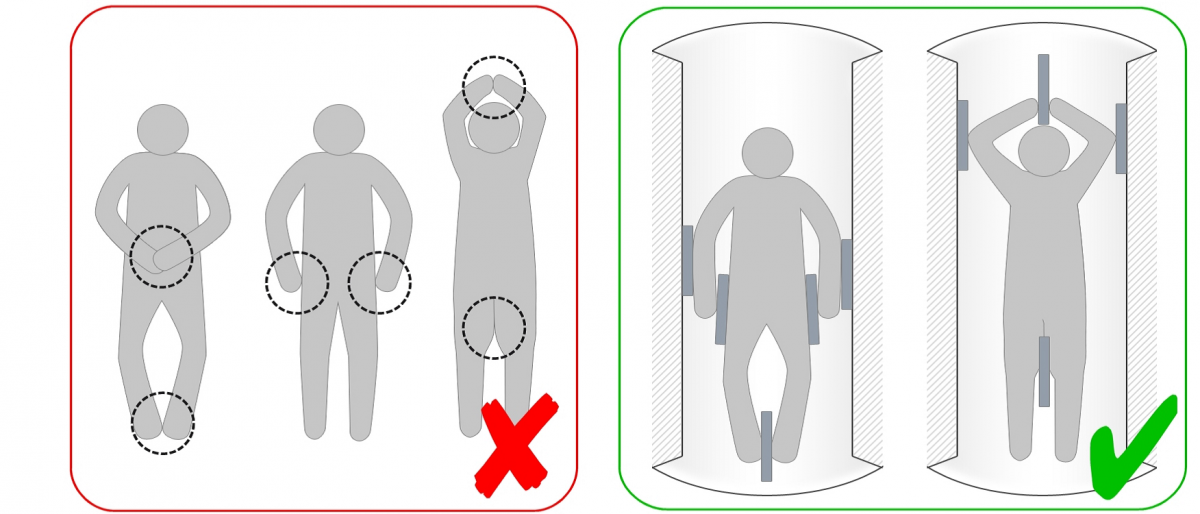
Ensure to prevent potential current loops as shown in the red labeled illustration.
Ensure the patient is positioned with proper distance (5 mm) to magnet tunnel as well as proper distance between parts of the body as shown in the green labeled illustration.
Additionally, if the subject is wearing electrically-conducting material peripheral nerve stimulation may occur –
- Have the participants change out of street clothes to light cotton clothing provided by the WIC.
- Have the participants removing their shoes before entering the magnet room.
- Ensure that the subject is free of metallic rings, chains, or electrically-conducting materials worked into items of clothing (for example zippers or brassiere support wires).
- Ensure that the participant does not wear clothing that is wet or dampened by perspiration.
- To prevent injuries, instruct the participants to remove makeup prior to the examination.
Hazards related to radio frequency (RF) fields
The RF field emitted during MR examinations induce electrical fields analogous to gradient fields. However, due to their high frequency they do not lead to stimulation effects in the electrically conductive body tissue. The energy exchange of the RF field leads primarily to warming. Exposure to high RF fields may cause excessive heating of skin and body tissue
- Instruct your subjects to press the squeeze ball in case of strong heat sensations.
- Use only covers (clothing, blankets, etc..) made of paper, cotton or linen.
An important value per body weight is the specific absorption rate or SAR, measured in watts/kg. The SAR limit is calculated for every subject by the subject's weight and the expected increase in body temperature for each imaging pulse sequence. The SAR values are monitored by an integrated SAR monitor on the MR console.
- To ensure correct calculation of the SAR values, the weight of the participant must be accurately entered during registration.
Subjects with poor thermo-regulatory systems must be carefully monitored
Looped cables (for example in RF coils, EEG lines etc) function as antennas and may warm to levels leading to skin burns at the points of contact. Current loops are also generated when the subject's skin contacts the tunnel lining or RF coil cables. To avoid this source for injury, special care has to be taken in correctly positioning especially adipose subjects.
- Route cables out of the scanner in a straight line. Don’t coil cables or allow them to touch the participant.
RF coils that are not correctly connected to the coil socket may warm considerably and cause burn hazards-> Ensure that all RF coils used are connected and remove disconnected RF coils from the patient table.
- Use only Normal Operating Mode
Equipment and Personal items
Only proven MR-compatible accessories should be used with the MR system. Accessory devices may be brought into the scanner room only after approval by the WIC staff.
Items may be tested for magnetic susceptibility with a hand-held magnet located at the MR facility.
Devices can be installed or brought into the MR room only after it has been approved in writing by the safety committee. Devices should be non-magnetic and should not introduce rf noise.
It is important to set up all the equipment in the scan room before the participant enters the room
Devices that are approved for use in the magnet room should be labeled accordingly.
Note: devices compatible with 1.5T systems may be unsuitable for 3T systems and or for 7T systems. Likewise, devices compatible with 3T systems may be unsuitable for 7T systems and vice versa..
Watches can not be brought into the MRI scan room since the magnetic field will render them inoperable. Devices with magnetically recorded information such as credit cards, cameras, phones, bank cards or data stored on magnetic tape will be erased if brought into the MRI scan room. Hearing aides may be damaged when exposed to the magnetic field.
Do not attempt to pull large magnetic objects (oxygen tanks) from a magnet field. The object may change its magnetic polarity and re-align itself on the magnet and become a projectile, causing a serious or fatal injury.
Operating Safely
When operating the MR equipment, be attentive to the following abnormal conditions:
- Louder-than-normal motor noises
- Sparks
- Components overheating
- Smoke or odors coming from the electronic equipment or from within the scan room.
- Change in magnet room temperature or humidity (should always be in the range: 18C - 22C, and humidity should not exceed 60%)
- If any of the above happens, it should be reported immediately to the WIC personnel.
Magnetic Field / Scan Room Emergencies
The magnet is equipped with two emergency buttons:
- Quenching the magnet button- Causes immediate collapse of the superconductive magnetic field. The magnetic filed collapses within 20 s
- Emergency - electricity stop / Shut Off - Turns off all incoming electrical power to the magnet
The nature of the emergency will dictate which procedure you follow. Each procedure has a distinct and specific purpose.
FAMILIARIZE YOURSELF WITH THESE BUTTONS. KNOW THEIR LOCATIONS AND THE DIFFERENCE!
Quench Button

 Quenching is a loss of superconductivity of the magnet coil due to a local temperature increase in the magnet as it becomes resistive, resulting in rapid evaporation of liquid helium via the exhaust line and quickly reducing the magnetic field strength.
Quenching is a loss of superconductivity of the magnet coil due to a local temperature increase in the magnet as it becomes resistive, resulting in rapid evaporation of liquid helium via the exhaust line and quickly reducing the magnetic field strength.
The time from activation of the emergency field shut down unit to the moment when the field strength in the magnet center has dropped to 20mT is typically 20s.
- A quench may happen spontaneously (for example when ramping up or filling the magnet, during an earthquake or fire or spontaneously without an obvious reason) or can be manually instigated in case of an emergency.
- Quenching may cause severe and irreparable damage to the superconducting coils (magnet).
- A magnet quench will result in several days’ downtime, so do not press the button except in a true emergency.
- Do not attempt to test this button!
The following situation is THE ONLY TIME that may require quenching of the magnet:
An accident involving large magnetic object pins or impales a person against the magnet and no other method can prevent further injury or free the person.
If the vent line fails in part or fully, gaseous helium will enter the examination room. In this case the air conditioning unit will not be able to ensure sufficient air exchange and the following hazardous situations may rise:
- Poor visibility due to strong fog in the room
- Rise in Pressure in the magnet room
- Hypothermia and risk of suffocation
- Following a quench, due to the above mentioned hazards, you must immediately remove the subject and all staff from the scan room.
Rescue attempts must not be performed by a single person.
Persons not directly involved in the rescue should leave the facility immediately !
Location of Quench Buttons at the WIC:
- One button is located in the alarm box, in the control room.
- One button is located at the entrance inside the examination room.
Emergency Stop / Shut Off Electricity Button
 Shutting power may be required for life threatening situations such as:
Shutting power may be required for life threatening situations such as:
- Fire in the computer room
- Fire, sparks, smoke in the scan room
- Flooding, water leaks
Keep in mind that when this button is pushed, it does not initiate a quench, the magnet remains “at field.” Make sure that all ferromagnetic materials remain outside of the scan room.
Location of Electricity – Stop Buttons at the WIC:
- One button is in the control room
- One button is located at the entrance to the examination room inside on the left side.
- One button is in the electronics room.
Table Stop Button
The table stop button is used to stop the table movement.
Push it immediately in case of accidents or risk of injury due to table movement, or if something gets caught. The table stop button disengages the table motor and allows a manual movement of the table.
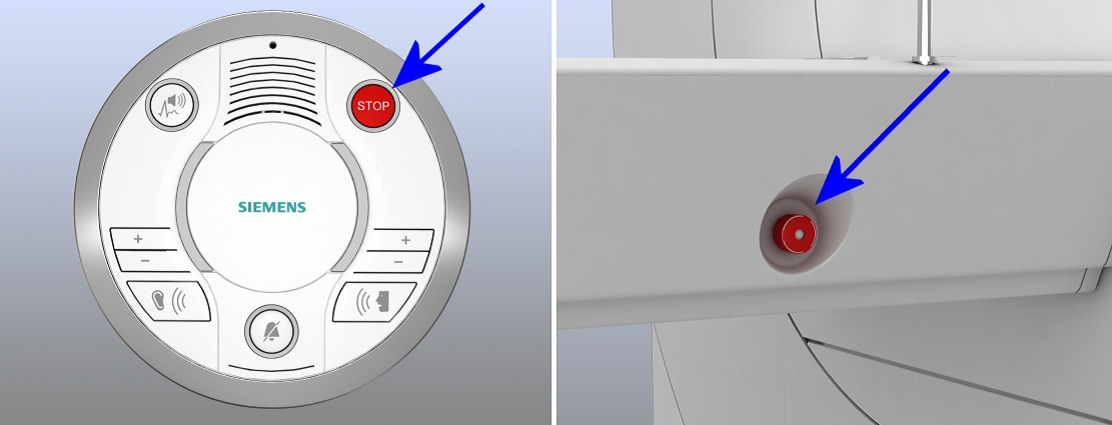 Two buttons are located on the magnet, on the control units, on both sides.
Two buttons are located on the magnet, on the control units, on both sides.- One button is located on the intercom.
In case of Fire:
Dial 2999 and report fire, smoke or suspicious smell.
Shut the electricity power and remember that the magnet is still "at field".
Subjects should be evacuated out from the building.
Close the scan room door to prevent the spread of the fire.
If emergency fire personnel need to enter the scan room to fight a fire, the emergency quench button must first be activated.
Alarm Box
Check the WARNING LED for alarm messages. Verify that the POWER LED is green. An alarm is present when yellow LED lights up and / or an alarm sounds.
In case of an alarm sound / or the presence of a WARNING LED lightening:
- Do not perform the MR examination
- Notify the WIC personnel and Siemens immediately.
Scanner Alarm messages
In case a scanner hardware error / an alarm appears an automatic shutdown will occur within 1 min. Then, the patient table motors can not be operated any longer.
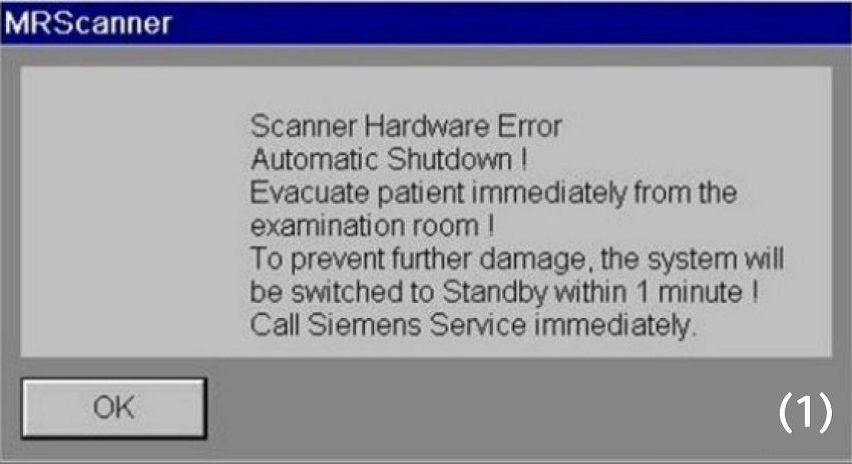
Evacuate the participant immediately from the magnet room by pressing the Home Position button.
In case of supervision malfunction is detected, a corresponding error msg appears:
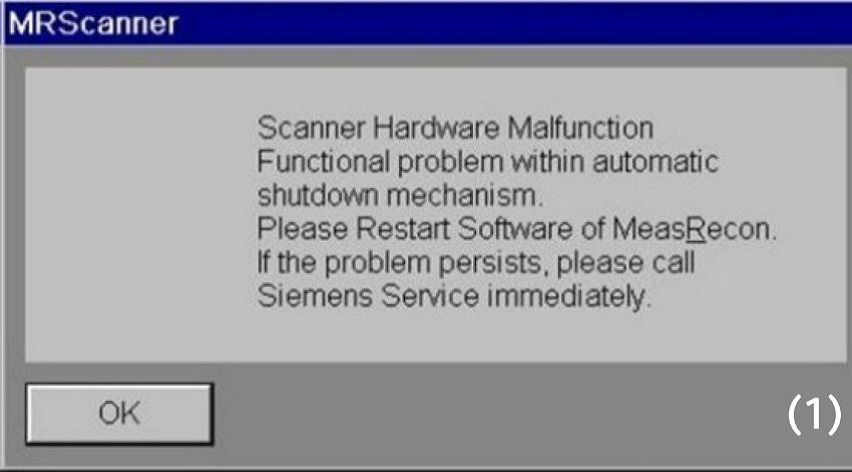
Please restart the system, and ensure that the patient’s table is outside before restarting the system.
If a dialog window is displayed informing that the helium fill level is too low:
Close the window, Stop the measurement and Notify WIC personnel.
Instructing the participants:
- Note safety instructions
- Inform the participants about the possible effects of MR examinations and the risk associated with the magnetic fields.
- Show the subjects how to activate the squeeze ball and ensure that the subject holds / can easily reach the squeeze bulb during the measurement
Cleaning
- Do not use cleaners or disinfectants containing alcohol or ether.
- Do not use hard or sharp objects (e.g. knives or tweezers) to remove residue.
- Clean the receptors with a commercially available cleaner.
Disinfecting system components
Components may only be cleaned with a semi-dry cloth.
Disinfect the system components with commercial disinfecting materials. However, do not use solutions with
alcohol or acetone.
Care and cleaning of floors
Do not use the following cleaning or care products:
- Sprays
- Silicon-based cleaning or care products
- Cleaning or care products with substances that release ammonia
- Cleaning or care products that destroy the anti-static properties of the floor covering
Phantom Fluids
The following measurement phantoms are available for quality assurance:
- Spherical phantom 170 mm in diameter (2570 cc), contains 1.25 gr NiSO4*6H2O per 1000 gr H2O dist.
- Green Plastic bottles (1900 cc), contain 3.75 gr NiSO4*6H2O + 5gr NaCl per 1000 gr H2O dist.
- Plastic bottle, 5300ml, containing 3.75 gr NiSO4*6H2O + 5gr NaCl per 1000 gr H2O dist.
- Blue spherical phantom 240 mm in diameter (7300 ml) contains MARCOL-Oil + 0.011 gr MACROLEX blue.
- Spherical Spectroscopic Phantom contains 8.2 gr NaC2H3O2 + 9.6 gr C3H3O3Li per 1000 ml H2O dist.
- ACR Phantom that includes 10mM NiCl2 and 75mM NaCl
Do not use damaged phantoms ! The phantom are all labeled and are stored in the scanner room.
Phantom fluid leaks may occur in case of improper use or damage to the phantom.
In case of spilled phantom fluid:
- Subjects should be immediately evacuated out from the scanner room.
- Put on protective clothing (gloves, lab coat, and goggles, and a mask if inhalable droplets are formed)
- Absorb the fluid immediately using absorbent material.
- Ensure that fluids from phantoms are disposed of properly. Collect the fluid in a plastic bucket and prevent phantom fluid from entering the waste water system.
- Avoid skin contact
- Change contaminated clothing and clean your hands thoroughly using soap and water.
First aid in case of contact with phantom fluid:
Skin contact: Thoroughly wash the area affected with soap and water. Contaminated clothing must be taken off immediately.
Eye contact: Keep the eyelid open and rinse the eyes under running water for at least 10-15 minutes
Aerosol inhaling: Immediately inhale fresh air and see a doctor if you feel sick. In case of NiSO4, see a doctor immediately.
Swallowing:
In case of swallowing of fluid from the water containing phantoms drink plenty of water and induce vomiting, consult a physician.
In case of swallowing of white oil: DO NOT induce vomiting. Ensure that the person lies still and immediately consult a physician.
In case of fire inform the fire department about the content of the measurement phantoms, and that the phantom fluids may produce nickelous aerosols.
REMEMBER! If any incident occurs within the MR scanner room, it must be reported as soon as possible to the WIC personnel.
